Interference in Thin Films
Interference in Thin Films: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Interference in Thin Films, Constructive Interference of Refracted Waves from Thin Film for Normal Incidence & Destructive Interference of Refracted Waves from Thin Film for Normal Incidence etc.
Important Questions on Interference in Thin Films
A thin film of soap solution lies on the top of a glass plate . When visible light is incident almost normal to the plate, two wavelengths and are strongly reflected. The minimum thickness(in ) of the soap solution is
When Two waves of same amplitude add constructively, the intensity becomes _____
What is the main principle used in Interference?
_____ does not show any interference pattern?
A soap film of refractive index 1.33 is illuminated by the light of wavelength at an angle of 45 degrees. There is complete destructive interference. For, find the thickness of the film.
Given Refractive index = 1.33, i =
When light is incident on a soap film of thickness , the wavelength of light reflected maximum in the visible region is . The refractive index of the film will be:
Interference fringes were produced in Young's double slit experiment using light of wavelength When a film of thickness was placed in front of one of the slits, the fringe pattern shifted by a distance equal to fringe-widths. The refractive index of the material of the film is
InYoung's double slit experiment, a mica sheet of thickness and refractive index is introduced in the path of ray from the first source . By how much distance the fringe pattern will be displaced :
A glass surface is coated by an oil film of uniform thickness The index of refraction of the oil is and that of the glass is . Some of the wavelengths in visible region are completely transmitted by the oil film under normal incidence. One of the wavelength transmitted completely in visible region is Find the value of .
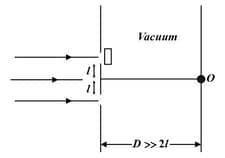
Three equidistant slits are illuminated by a monochromatic parallel beam of light falling normally onto them. The screen is parallel to the plane of the slits and the slit separation the slit-screen separation. The observation point is directly opposite It is given that being the wavelength of light. Find the ratio of the intensity at when all slits are open to the intensity at when only one slit is open.
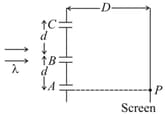
In , let and be two slits as shown. Thin films of thickness and and refractive indices and are placed in front of and respectively. If then the central maxima will
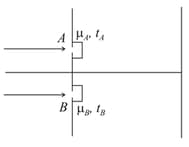
If thickness of thin film is made extremely thin then film will appeared :-
If the wavelength of incident light on a soap film is then its minimum thickness so that constructive interference in reflected light can be observed. The value of is then find the value of .[Take refractive index of the film as ]
A quartz plate of thickness introduces a phase difference of between ordinary and extraordinary light. Write value of where is the greatest integer function. [Take and ].
A lens made out of a material of refractive index, is coated with a thin film of refractive index in order to reduce the reflection from its surface at . The minimum thickness of the film which will minimise the intensity of the reflected light is (assume near normal incidence)
Which of the following is compound?
In Young's double-slit experiment, both the slits produce equal intensities on a screen. A transparent thin film of refractive index is kept in front of one of the slits, due to which the intensity at the point on the screen becomes of its initial value. If the wavelength of monochromatic light is , then what is the minimum thickness (in ) of the film?
In Young's experiment, monochromatic light is used to illuminate the two slits and . Interference fringes are observed on a screen placed in front of the slits. Now if a thin glass plate is placed normally in the path of the beam coming from the slit, then which of the following explanation holds true with regards to fringes/fringe width?
A thin layer of oil (index of refraction and thickness ) floats on the surface of the liquid (index of refraction ). Now, white light is normally incident on the thin film of oil. Of the following, the most reflected wavelength is
Consider a case of thin film interference as shown in the figure. Thickness of film is equal to wavelength of light in